What are the principles of relay protection and the four properties?
1.The principle of relay protection
Relay protection is mainly the use of power system components in the occurrence of short-circuit or abnormal conditions of electrical quantities (current, voltage, power, frequency, etc.) changes constitute the principle of relay protection action, there are other physical quantities, such as transformer tank failure accompanied by the production of a large number of gas and oil flow rate increases or the increase in oil pressure strength. In most cases, regardless of which physical quantity is reacted, the relay protection device includes a measuring part (and fixed value adjustment part), a logic part, and an execution part.
(A) Parameters in power system operation
(e.g., current, voltage, power factor angle) are distinctly different during normal operation and fault conditions. Relay protection device is the use of these parameters of change, in reflection, detection based on the judgment of the nature and scope of the power system fault, and then make the appropriate response and processing (such as issuing a warning signal or make the circuit breaker trip, etc.).
(B) the principle of relay protection device analysis
(1) Sampling unit
It will be protected by the operation of the power system physical quantities (parameters) after electrical isolation and converted to relay protection device in the comparison of the identification unit can accept the signal, by one or several sensors such as current, voltage transformer.
(2) Comparison and identification unit
Including the given unit, the signal from the sampling unit and the given signal comparison, so that the next level of processing unit to send what kind of signal. (Normal state, abnormal state or fault state) Comparison and identification unit can be composed of four current relays, two for quick-break protection, the other two for overcurrent protection.
The setting value of the current relay is the given unit, the current coil of the current relay receives the current signal from the sampling unit (current transformer), when the current signal reaches the setting value of the current, the current relay operates and sends out a signal to the next level processing unit to make the circuit breaker finally turn off; if the current signal is smaller than the setting value, the current relay does not operate, and the signal to the next level unit does not operate either. If the current signal is smaller than the set value, the current relay will not operate and the signal transmitted to the lower unit will not operate. Identify the comparative signal "quick break", "overcurrent" information is transmitted to the next unit processing.
(3) Processing unit
Accept the signals from the comparison and identification unit, process them according to the requirements of the comparison and identification unit, according to the size, nature and combination of the output of the comparison link in the order of appearance, to determine whether the protective device should be acted upon; composed of time relays, intermediate relays and so on. Current protection: quick break - intermediate relay action, overcurrent, time relay action.
(4) Execution unit
Fault handling through the implementation of the implementation of the unit. Execution unit is generally divided into two categories: one is the sound, light signal relay; (such as electric flute, electric bell, flash signal lamp, etc.) Another type of circuit breaker for the operating mechanism of the breaking coil, so that the circuit breaker breaks.
(5) Control and operation power supply
Relay protection device requires its own independent AC or DC power supply, and the power supply power also increases or decreases due to the number of controlled devices; AC voltage is generally 220 volts, 110V; see "GB50053-2013 20kV and the following substation design specifications".
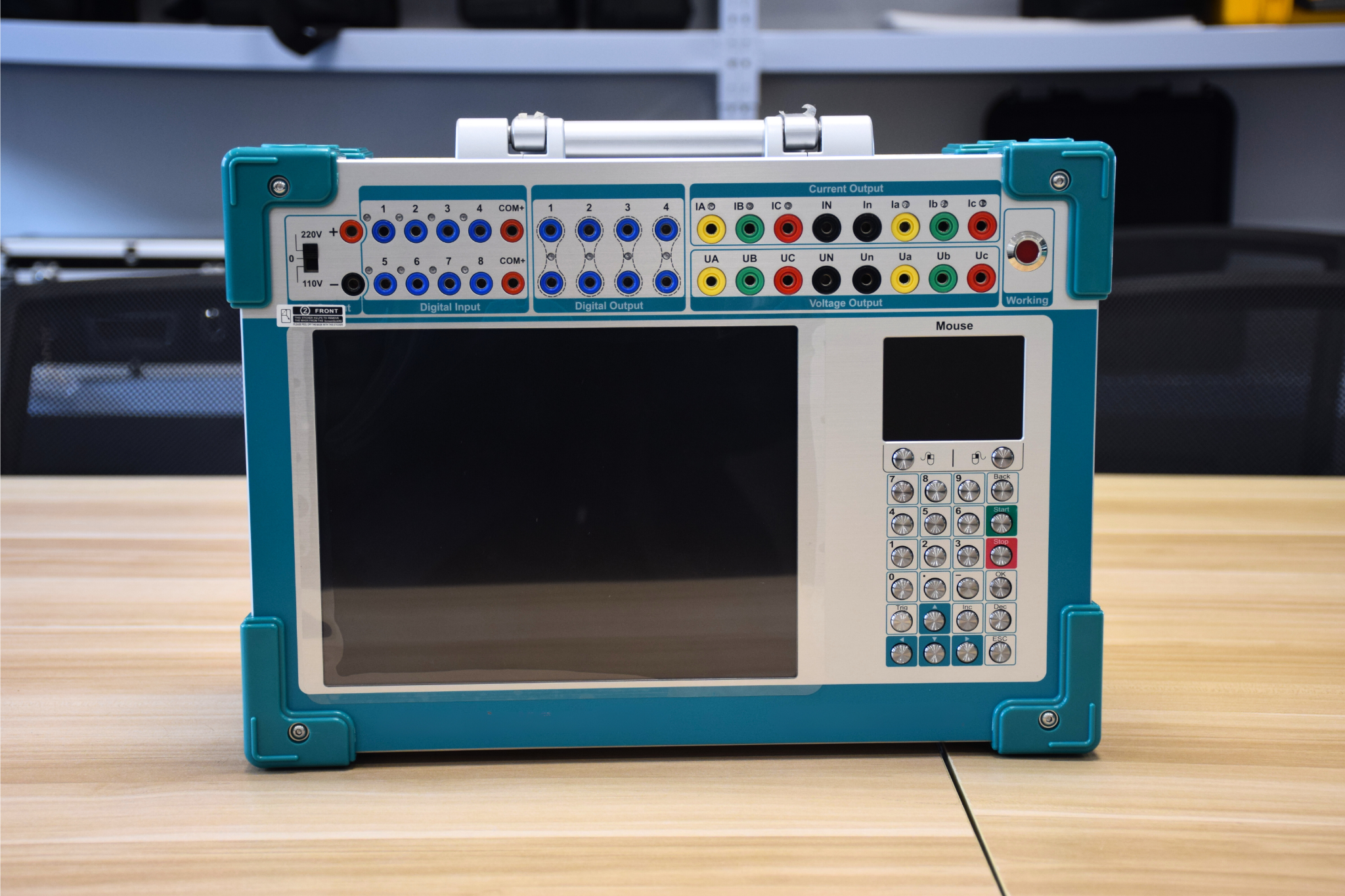
RDJB-1600K Microcomputer Relay Protection Test Kit is our company extensively listening to user opinions, summarizing the advantages and disadvantages of similar domestic products at present, and fully using modern advanced A new type of miniaturized microcomputer relay protection tester based on microelectronic technology and devices. Small size and high accuracy.
Click on the product model number RDJB-1600K for more product details and parameters.
To get a quote click on Contact Us.
2. The four nature of relay protection
Action on the trip relay protection, technology should generally meet the four basic requirements: selectivity, speed, sensitivity, reliability.
(1) Reliability
Refers to the protection of the action when the action, should not be action when the action, that is, neither false action nor refusal to act, to ensure that the removal of faulty equipment or lines.
(2) sensitivity
Refers to the equipment or line within the scope of protection of the occurrence of metallic short-circuit, the protective device should have the necessary sensitivity factor. Ensure that there is a fault on the resection.
Refers to the ability to react to fault conditions within the specified protection range. A protective device that meets the sensitivity requirements shall be able to react sensitively and correctly to a fault within the zone, regardless of the location of the short-circuit point and the type of short-circuit.
Typically, sensitivity is measured by the sensitivity factor and denoted as Klm.
where the minimum and maximum calculated values of the fault parameters are based on the actual possible most unfavorable mode of operation, type of fault and short-circuit point.
In the Technical Regulations for Relay Protection and Safety Automatic Devices GB/T 14285-2016, the requirements for the sensitivity coefficient Klm for each type of protection are specified.
(3) Selectivity
It means that the fault is first removed by the protection of the faulty equipment or line itself, and when the protection or circuit breaker of the faulty equipment or line itself refuses to operate, only then is it permitted to remove the fault by the protection of the adjacent equipment or line or the protection of the circuit breaker failure. Avoid large-scale power outages.
Selectivity means that when a power system fault occurs, the protective device will only remove the faulty component, while allowing the non-faulty component to still operate normally, in order to minimize the scope of power outages.
Selectivity is that the point of fault in the zone on the action, outside the zone does not act. When the main protection does not operate, the fault is removed by the near backup or far backup to minimize the outage area. Because the far backup protection is more complete (on the protection device DL, secondary circuit and DC power supply faults caused by the refusal of action are backup) and the realization of a simple, economic, should be given priority to use.
(4) fast-acting
Refers to the protective device should be able to remove the short-circuit fault as soon as possible. The purpose is to improve system stability, reduce the degree of damage to faulty equipment and lines, reduce the scope of the fault, improve the automatic reclosing and backup power or standby equipment automatically put into effect.
Rapid fault removal. Improve system stability; reduce the action time of the user under low voltage; reduce the degree of damage to faulty components to avoid further expansion of the fault.
General fast protection action time of 0.06 to 0.12s, the fastest up to 0.01 to 0.04s.
General circuit breaker action time of 0.06 ~ 0.15s, the fastest up to 0.02 ~ 0.06s.
Relay protection basic task is: when the power system failure or abnormal conditions, in the shortest possible time and the smallest possible area, automatically remove the faulty equipment from the system, or send a signal from the duty officer to eliminate the root cause of abnormal conditions, in order to reduce or avoid equipment damage and the impact of power supply to adjacent areas.
The above four basic requirements are the basis for the design, configuration and maintenance of relay protection, and is the basis for analyzing and evaluating relay protection. These four basic requirements are interrelated, but often contradictory. Therefore, in practice, according to the structure of the grid and the nature of the user, dialectical unification.
3.The sequence of the four properties
(1) Reliability
(2) Sensitivity
(3) Selectivity
(4) Rapidity.
4.The contradictory nature of the four
(1) sensitivity and reliability are contradictory.
If you want to meet the sensitivity, the protection action value can not be set too high. But if the protection is too low, the protection may be unreliable. For example, when overloaded, the protection will be activated when disturbed.
(2) Selectivity and rapidity are contradictory.
Current protection is generally divided into three sections of protection, which three sections have a problem of cooperation, depending on the protection of different plant and different time to match. This will need to rely on time to avoid the problem of cross-protection area, such as a protection time of 200ms, two generally take 500ms, when a failure to rely on the second paragraph to action, 500ms of time can not meet the requirements of the rapidity of action.




