Purpose and test method of AC withstand voltage test for transformer
1. Purpose of the test
It is the most effective way to identify the insulation strength of transformers, and is also an important test item to ensure the safe operation of transformers and avoid insulation accidents. The AC withstand voltage test can detect the moisture and concentrated defects of the transformer main insulation, such as cracking of the winding main insulation, loose displacement of the winding, insufficient lead insulation distance, dirt attached to the insulation, etc.
RDS51052 AC/DC withstand voltage tester is a universal AC/DC high-voltage withstand voltage tester with an output voltage of 0-5 (kV). It is widely used for withstand voltage testing of electrical equipment, gluewood appliances, piezoelectric ceramics, various household appliances, and instruments.
For more product details, please click RDS51052.
For the latest quote, please contact us.
AC withstand voltage test is a destructive test in insulation test. It can only be carried out after other non-destructive tests (such as insulation resistance and absorption ratio test, DC leakage test, dielectric loss tangent and insulation oil test) are qualified. After this test is passed, the transformer can be put into operation. AC withstand voltage test is a key test, so the preventive test regulations stipulate that transformers of 10kV and below should be subjected to AC withstand voltage test after 1 to 5 years, 66kV and below after overhaul, after replacing windings, and when necessary.
2. Test methods
(I) Test connection
The AC withstand voltage test connection for small and medium-sized power transformers below 35kV is shown in the figure. In the figure, the control, protection and monitoring parts of the low-voltage side of the test transformer are not drawn.
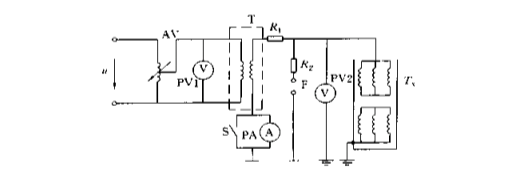
Each phase winding should be tested. During the test, the lead wires of each phase winding should be short-circuited together. If there are lead wires at the center point, the lead wires should also be short-circuited together with the three phases.
(II) Test voltage
According to the acceptance test standard, transformers with a capacity of less than 8000kVA and a winding rated voltage of less than 110kV should be subjected to AC withstand voltage test according to the test voltage standards listed in Appendix 1 of the standard.
The preventive test regulations stipulate that the test voltage values for oil-immersed transformers are detailed in Table 6 of the regulations (the voltage value for periodic tests is based on partial winding replacement). When all windings of dry-type transformers are replaced, the factory test voltage value shall be used; when partially replacing windings and conducting periodic tests, the factory test voltage value shall be 0.85 times the factory test voltage value.
(III) Precautions
In addition to the general precautions for AC withstand voltage test, the following points should be noted according to the characteristics of the transformer:
1) The test transformer must be equipped with an overcurrent protection tripping device.
2) The AC withstand voltage test of a three-phase transformer does not need to be carried out in phases. However, all the three-phase lead wires of the same winding must be short-circuited before the test, otherwise it will not only affect the accuracy of the test voltage, but may even endanger the main insulation of the transformer (see Question 9 of this chapter for detailed analysis).
3) The preventive test regulations point out that for fully insulated transformers below 66kV, when on-site conditions are not available, only external construction frequency withstand voltage tests can be carried out.
4) For power transformers with weaker neutral insulation than other parts or graded insulation, the above-mentioned external AC withstand voltage test cannot be used, but an induction withstand voltage test of 1.3 times the rated voltage should be used.
5) The test must be carried out after being filled with qualified oil and stationary for a certain period of time.
6) For medium and small capacity transformers with a voltage level of 35kV, the test voltage is allowed to be measured on the low-voltage side of the test transformer. For power transformers with larger capacity, in order to make the measurement accurate and reliable, a voltage transformer or an electrostatic voltmeter should be used to directly measure the test voltage on the high-voltage side.
7) If discharge or breakdown occurs during the test, the voltage should be reduced immediately. Cut off the power supply to avoid expanding the fault.





